Introduction to DBMS
Introduction to Database Management System (DBMS)
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software system designed to manage, store, retrieve, and manipulate data in a structured manner. It acts as an intermediary between users and the underlying data, providing a systematic and organized approach to handling information. Here are key aspects of DBMS:
1. Purpose and Importance:
- DBMS is employed to manage data efficiently, ensuring data integrity, security, and accessibility.
- It serves as the foundation for various applications, from basic contact management systems to complex enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions.
2. Data Organization:
- DBMS organizes data into structured formats, primarily tables, with predefined data types.
- Data relationships and dependencies are defined to facilitate efficient querying and data retrieval.
3. Data Independence:
- DBMS abstracts data from the underlying storage and access mechanisms, offering both logical and physical data independence.
- Logical data independence means changes to the data structure do not impact applications, and physical data independence ensures that data can be relocated without affecting application logic.
4. Data Retrieval and Query Language:
- DBMS provides a query language (e.g., SQL - Structured Query Language) for users to interact with data.
- Users can write queries to retrieve, update, and manipulate data based on their requirements.
5. Security and Access Control:
- DBMS offers features for securing data, including user authentication, authorization, and encryption.
- Data access control ensures that only authorized users can access, modify, or delete specific data.
6. Data Integrity and Constraints:
- DBMS enforces data integrity constraints (e.g., primary keys, foreign keys) to maintain data consistency.
- Constraints help ensure data accuracy and adherence to predefined rules.
7. Scalability and Performance:
- DBMS systems are designed to scale as data volumes grow, with features such as indexing, caching, and query optimization to enhance performance.
8. Recovery and Backup:
- DBMS provides mechanisms for data recovery and backup, helping to restore data in case of failures or errors.
- Features like transaction logging and point-in-time recovery support data durability.
9. Concurrency Control:
- DBMS manages concurrent access to data, ensuring that multiple users can work on the database simultaneously without data corruption or inconsistencies.
10. Transaction Management:
- DBMS supports transactions, which are sequences of database operations that are executed as a single unit.
- Transactions follow the ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) to ensure reliable data processing.
11. Data Modeling:
- DBMS encourages the use of data models to represent data structures and their relationships.
- Common data models include the hierarchical model, network model, and relational model.
12. Types of DBMS:
- There are different types of DBMS, including relational DBMS (RDBMS), NoSQL DBMS, object-oriented DBMS, and more.
- RDBMS, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle, use structured tables and SQL for data manipulation.
13. Advantages of DBMS:
- Centralized data management, reduced data redundancy, data security, improved data access, data integrity, and data consistency are among the advantages of DBMS.
14. Challenges and Considerations:
- Selecting the right DBMS for specific applications, addressing scalability issues, optimizing database performance, and ensuring data privacy and security are common challenges in DBMS implementation.
In summary, DBMS plays a vital role in organizing and managing data for various applications, offering a structured and efficient approach to data storage and retrieval.
DBMS Architecture
- The DBMS design depends upon its architecture. The basic client/server architecture is used to deal with a large number of PCs, web servers, database servers and other components that are connected with networks.
- The client/server architecture consists of many PCs and a workstation which are connected via the network.
- DBMS architecture depends upon how users are connected to the database to get their request done.
Types of DBMS Architecture
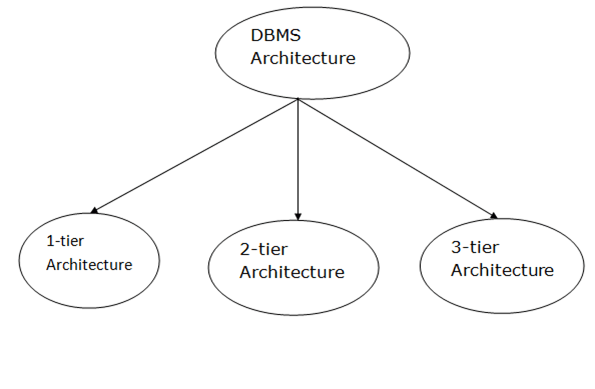
Database architecture can be seen as a single tier or multi-tier. But logically, database architecture is of two types like: 2-tier architecture and 3-tier architecture.
1-Tier Architecture
- In this architecture, the database is directly available to the user. It means the user can directly sit on the DBMS and uses it.
- Any changes done here will directly be done on the database itself. It doesn't provide a handy tool for end users.
- The 1-Tier architecture is used for development of the local application, where programmers can directly communicate with the database for the quick response.
2-Tier Architecture
- The 2-Tier architecture is same as basic client-server. In the two-tier architecture, applications on the client end can directly communicate with the database at the server side. For this interaction, API's like: ODBC, JDBC are used.
- The user interfaces and application programs are run on the client-side.
- The server side is responsible to provide the functionalities like: query processing and transaction management.
- To communicate with the DBMS, client-side application establishes a connection with the server side.\
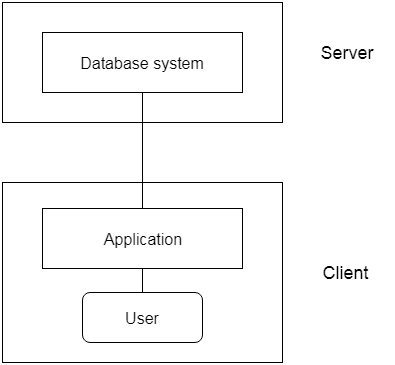
Fig: 2-tier Architecture
3-Tier Architecture
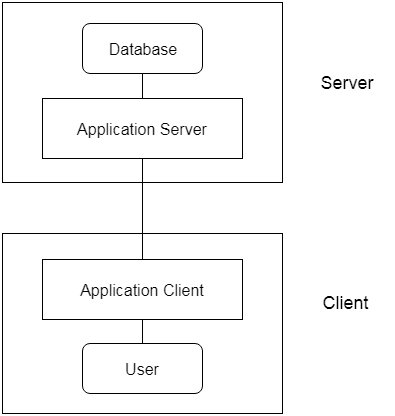
- The 3-Tier architecture contains another layer between the client and server. In this architecture, client can't directly communicate with the server.
- The application on the client-end interacts with an application server which further communicates with the database system.
- End user has no idea about the existence of the database beyond the application server. The database also has no idea about any other user beyond the application.
- The 3-Tier architecture is used in case of large web application.
Data Models
A data model is a conceptual representation of data that defines how data is organized, stored, and accessed in a database management system (DBMS). It serves as a bridge between the real-world entities and the physical storage of data in a DBMS. Data models provide a way to describe and structure data, making it easier to manage and understand. Here are some key aspects of data models:
1. Purpose of Data Models:
- Data models are essential for designing and structuring databases in a way that accurately represents the data and its relationships.
- They help in creating a clear and consistent structure for data, facilitating data retrieval, modification, and analysis.
2. Common Types of Data Models:
- Relational Data Model: The relational model represents data as tables (relations) with rows (tuples) and columns (attributes). It is widely used in relational database management systems (RDBMS) like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
- Hierarchical Data Model: In this model, data is organized in a tree-like structure, with parent-child relationships. It is used in some database systems, especially in hierarchical databases.
- Network Data Model: The network model extends the hierarchical model by allowing multiple parent-child relationships. It is used in network databases.
- Object-Oriented Data Model: This model represents data as objects with attributes and methods. It is used in object-oriented databases.
- Entity-Relationship (E-R) Data Model: The E-R model represents data as entities, attributes, and relationships. It is widely used for designing relational databases.
3. Components of Data Models:
- Entities: Entities are real-world objects, concepts, or events that are represented in the data model. For example, in a library database, books, authors, and borrowers could be entities.
- Attributes: Attributes are properties or characteristics of entities. In the library database, attributes of a book could include ISBN, title, and publication date.
- Relationships: Relationships define how entities are connected or associated with each other. In the library database, there would be relationships between books and authors, books and borrowers, etc.
4. Diagrams and Notations:
- Data models are often represented graphically using diagrams. Common notations include entity-relationship diagrams (ERD) for the E-R model and tables with rows and columns for the relational model.
5. Abstraction Levels:
- Data models can be categorized into different abstraction levels:
- Conceptual Data Model: This represents the high-level, abstract view of data without concern for implementation details.
- Logical Data Model: The logical model focuses on defining the structure and relationships of data, usually without considering specific database management systems.
- Physical Data Model: The physical model defines how data is actually stored in a database, including details such as data types and indexing.
6. Data Normalization:
- Data normalization is the process of organizing data in a relational database to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity. It involves breaking down data into related tables and defining relationships.
7. Benefits of Data Models:
- Data models provide a clear and structured way to represent data, making it easier to design databases and understand data relationships.
- They facilitate communication between database designers, developers, and users.
- Data models help ensure data consistency, accuracy, and data integrity.
8. Challenges:
- Creating effective data models can be challenging and requires a deep understanding of the data and its relationships.
- Changes in data requirements or business rules may necessitate modifications to the data model.
9. Evolving Data Models:
- Data models can evolve over time to accommodate changing data requirements, technology advancements, and business needs.
Effective data modeling is a crucial step in database design, ensuring that data is well-structured, accurate, and efficiently stored and retrieved. Different data models are chosen based on the specific requirements and characteristics of the data and the applications that use it.
Entity-Relationship (E-R) Diagram
An Entity-Relationship (E-R) diagram is a visual representation of the data model that uses entities, attributes, and relationships to describe the structure of a database. E-R diagrams are widely used for designing relational databases and are a key tool in the field of database management. Here's a detailed explanation of E-R diagrams:
1. Entities:
- Entities are objects or concepts in the real world that are represented in the database. Each entity is typically depicted as a rectangular box in an E-R diagram.
- Entities can represent concrete objects (e.g., a customer, a product) or abstract concepts (e.g., an order, a transaction).
2. Attributes:
- Attributes are properties or characteristics of entities. They provide details about entities and are represented as ovals or ellipses connected to their respective entities.
- For example, if an entity represents a "student," attributes might include "student ID," "name," "date of birth," and "email address."
3. Relationships:
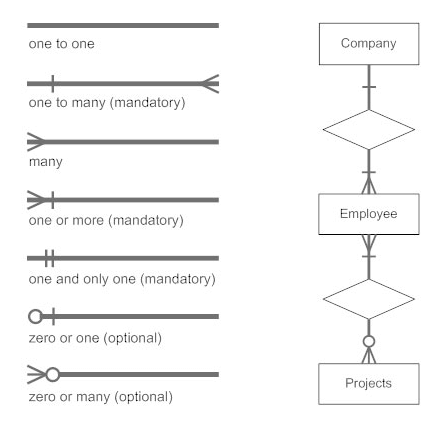
- Relationships describe how entities are related to each other within the database. They are depicted as diamond shapes connecting entities.
- Relationships can be one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many, indicating the cardinality of the relationship.
- For instance, in an E-R diagram for a library database, there might be a "BORROWS" relationship between the "STUDENT" entity and the "BOOK" entity.
4. Cardinality and Multiplicity:
- Cardinality and multiplicity indicate the number of instances of one entity that are related to the number of instances of another entity through a relationship.
- For example, in a one-to-many relationship between "AUTHOR" and "BOOK," an author can write many books, but each book is written by one author.
5. Key Attributes:
- Key attributes are attributes that uniquely identify instances of an entity. In an E-R diagram, they are typically underlined.
- For example, in an "EMPLOYEE" entity, the "EmployeeID" attribute might serve as the key attribute.
6. Weak Entities:
- Some entities, known as weak entities, do not have a unique key attribute. They rely on a related strong entity to provide their identity.
- Weak entities are typically represented with a double rectangle in an E-R diagram.
7. Superclass and Subclass (Inheritance):
- In E-R diagrams, you can depict the concept of inheritance, where a superclass (parent entity) has subclasses (child entities) that inherit attributes and relationships from the superclass.
- For instance, a "VEHICLE" superclass might have subclasses "CAR" and "MOTORCYCLE" with their specific attributes.
8. Participation Constraints:
- Participation constraints indicate whether entities are required to participate in a relationship (total participation) or if participation is optional (partial participation).
9. Modifying Relationships:
- Relationships can be modified with labels, such as "owns," "manages," or "enrolls," to provide additional information about the nature of the relationship.
10. Diagram Notations:
- E-R diagrams use various notations, symbols, and lines to represent entities, attributes, relationships, and cardinality.
- Crow's Foot notation and Chen notation are two common styles of E-R diagram notation.
11. Use Cases:
- E-R diagrams are used during the design phase of a database to illustrate the structure of the database, including tables, keys, and relationships.
- They serve as a visual aid for database designers and developers to understand and communicate the database schema.
12. Database Implementation:
- E-R diagrams are an important step in the process of designing and implementing a database. Once the E-R diagram is created, it can be translated into a physical database schema, complete with tables, keys, and data types.
E-R diagrams play a vital role in database design and communication between stakeholders. They help ensure that the database accurately represents the real-world entities and their relationships, leading to well-structured and efficient database systems.
Relational Database Design
Relational database design is the process of structuring data in a way that ensures data integrity, accuracy, and efficiency within a relational database management system (RDBMS). It involves creating tables, defining relationships, and establishing constraints to store and retrieve data effectively. Here's a comprehensive explanation of relational database design:
1. Understanding Data Requirements:
- The first step in relational database design is understanding the data requirements of the system or application.
- This involves identifying the entities, attributes, and relationships that need to be represented in the database.
2. Entity-Relationship Diagram (E-R Diagram):
- A crucial step in database design is creating an Entity-Relationship (E-R) diagram to visualize the entities, attributes, and relationships.
- The E-R diagram serves as a blueprint for designing the database tables.
3. Normalization:
- Normalization is the process of organizing data in a relational database to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity.
- It involves decomposing large tables into smaller ones, ensuring that each table represents a single, well-defined entity or concept.
4. Primary Keys:
- Each table in a relational database must have a primary key. A primary key is a unique identifier for the records in the table.
- It ensures that each record in the table is distinguishable and that data integrity is maintained.
5. Foreign Keys:
- Foreign keys are used to create relationships between tables. A foreign key in one table references the primary key in another table.
- This establishes the relationships and enforces referential integrity, ensuring that data in related tables remains consistent.
6. Data Types and Constraints:
- For each attribute in a table, you need to specify the data type, such as text, number, date, or boolean.
- Constraints, such as unique constraints, check constraints, and default values, can be applied to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
7. Indexing:
- Indexes are used to speed up data retrieval operations. They provide a quick way to locate records based on certain columns.
- Indexing is essential for optimizing query performance.
8. Database Normal Forms:
- Relational databases should adhere to specific normal forms to minimize data redundancy and anomalies. Common normal forms include 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF.
9. Denormalization:
- While normalization reduces data redundancy, there are cases where denormalization is necessary for performance reasons.
- Denormalization involves introducing redundancy into the database to optimize query performance.
10. Database Diagram:
- After defining the tables, keys, relationships, and constraints, a database diagram can be created to illustrate the complete database schema.
11. Implementing the Database:
- Once the database design is finalized, it can be implemented in the chosen RDBMS, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server.
- Tables are created, and data is inserted according to the design.
12. Testing and Optimization:
- Database design should be tested thoroughly to ensure that it meets the data requirements and performs efficiently.
- Performance optimization, query tuning, and indexing may be necessary.
13. Maintenance and Updates:
- Ongoing database maintenance involves tasks such as data backup, data migration, and schema updates to accommodate changing data requirements.
14. Data Security:
- Security measures, such as user authentication, access control, and encryption, should be implemented to protect the database.
Relational database design is a structured and iterative process that requires a deep understanding of data requirements and relationships. Well-designed databases play a critical role in the success of software applications and data-driven businesses by ensuring data accuracy, integrity, and efficient data retrieval.