Unit 4 : Testing & Implementation
- Software testing fundamentals
- Internal and external views of Testing
- White box testing (basis path testing, control structure testing)
- Black box testing
- Regression Testing
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- Validation Testing
- System Testing and Debugging
- Software Implementation Techniques (Coding practices, Refactoring)
Software Testing Fundamentals
Software testing can be stated as the process of verifying and validating whether a software or application is bug-free, meets the technical requirements as guided by its design and development, and meets the user requirements effectively and efficiently by handling all the exceptional and boundary cases.
The process of software testing aims not only at finding faults in the existing software but also at finding measures to improve the software in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and usability. It mainly aims at measuring the specification, functionality, and performance of a software program or application.
Software testing can be divided into two steps:
-
Verification: it refers to the set of tasks that ensure that the software correctly implements a specific function.
-
Validation: it refers to a different set of tasks that ensure that the software that has been built is traceable to customer requirements.
Verification: “Are we building the product right?”
Validation: “Are we building the right product?”
Software Testing can be broadly classified into two types:
- Manual Testing: Manual testing includes testing software manually, i.e., without using any automation tool or any script. In this type, the tester takes over the role of an end-user and tests the software to identify any unexpected behavior or bug. There are different stages for manual testing such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing.
Testers use test plans, test cases, or test scenarios to test software to ensure the completeness of testing. Manual testing also includes exploratory testing, as testers explore the software to identify errors in it.
- Automation Testing: Automation testing, which is also known as Test Automation, is when the tester writes scripts and uses another software to test the product. This process involves the automation of a manual process. Automation Testing is used to re-run the test scenarios quickly and repeatedly, that were performed manually in manual testing.
Apart from regression testing, automation testing is also used to test the application from a load, performance, and stress point of view. It increases the test coverage, improves accuracy, and saves time and money when compared to manual testing.
Different Software Testing Techniques
Software testing techniques can be majorly classified into two categories:
-
Black Box Testing: The technique of testing in which the tester doesn’t have access to the source code of the software and is conducted at the software interface without any concern with the internal logical structure of the software is known as black-box testing.
-
White-Box Testing: The technique of testing in which the tester is aware of the internal workings of the product, has access to its source code, and is conducted by making sure that all internal operations are performed according to the specifications is known as white box testing.
| Aspect | Black Box Testing | White Box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge of Internal Workings | Not Required | Knowledge of Internal Workings is a Must |
| Also Known As | Closed Box / Data-Driven Testing | Clear Box / Structural Testing |
| Typical Participants | End Users, Testers, and Developers | Primarily Testers and Developers |
| Testing Approach | Trial and Error Method | Analyzes Data Domains and Internal Boundaries |
| Focus on Application's Functionalities | Yes | Yes (in addition to internal structures) |
| Code-Level Testing | No | Yes |
| Testing Strategy | Tests based on Requirements and Inputs | Tests based on Code Structure and Logic |
| Testing Timeframe | Mostly at the End of Development | Throughout Development Lifecycle |
| Finding Hidden Issues | Limited due to Lack of Code Knowledge | Better Suited for Finding Hidden Issues |
| Design and Code Improvement | Less Influence | Can Contribute to Design and Code Improvement |
Levels of Software Testing
Software level testing can be majorly classified into 4 levels:
-
Unit Testing: A level of the software testing process where individual units/components of a software/system are tested. The purpose is to validate that each unit of the software performs as designed.
-
Integration Testing: A level of the software testing process where individual units are combined and tested as a group. The purpose of this level of testing is to expose faults in the interaction between integrated units.
-
System Testing: A level of the software testing process where a complete, integrated system/software is tested. The purpose of this test is to evaluate the system’s compliance with the specified requirements.
-
Acceptance Testing: A level of the software testing process where a system is tested for acceptability. The purpose of this test is to evaluate the system’s compliance with the business requirements and assess whether it is acceptable for delivery.
Internal & External Testing
INTERNAL TESTING
The main advantage of such type of testing is the ability to control the whole process and to address issues at once.
The main disadvantage is that in-house testing is much more expensive than outsourced one. (There are hideaway spending: expenses on hiring, training people and supporting the full-time team even if you do not need its service at the moment).
• Continuously working on the same application is a monotonous activity, so the team loses the ability to think out of the box and the probability of finding bugs is reduced.
EXTERNAL TESTING
The main advantage is that external testing will help you to reduce your costs.
Also:
• External testing provides you with certified, experienced specialists round the clock.
• Flexibility (the team size can be changed, based on the customer requirements).
• Prices on outsourced testing are reasonable.
• Fresh eyes (independent testers are focused on finding bugs, while in-house team are focused on fulfilling the requirements)
• At any point in time, an external tester knows "how many scenarios for a particular functionality have been executed?" whereas internal testers are just solely relying on test cases. Apart from this, external testers get a relatively stable product to test. Thanks to the internal testing team. So, they can focus on what they are targeting to test. There are hardly any distractions because of which they can lose focus.
White Box Testing
The box testing approach of software testing consists of black box testing and white box testing. We are discussing here white box testing which also known as glass box is testing, structural testing, clear box testing, open box testing and transparent box testing. It tests internal coding and infrastructure of a software focus on checking of predefined inputs against expected and desired outputs. It is based on inner workings of an application and revolves around internal structure testing. In this type of testing programming skills are required to design test cases. The primary goal of white box testing is to focus on the flow of inputs and outputs through the software and strengthening the security of the software.
The term 'white box' is used because of the internal perspective of the system. The clear box or white box or transparent box name denote the ability to see through the software's outer shell into its inner workings.
The white box testing contains various tests, which are as follows:
- Path testing
- Loop testing
- Condition testing
- Testing based on the memory perspective
- Test performance of the program
Path testing
In the path testing, we will write the flow graphs and test all independent paths. Here writing the flow graph implies that flow graphs are representing the flow of the program and also show how every program is added with one another
Loop testing
In the loop testing, we will test the loops such as while, for, and do-while, etc. and also check for ending condition if working correctly and if the size of the conditions is enough.
Condition testing
In this, we will test all logical conditions for both true and false values; that is, we will verify for both if and else condition.
Testing based on the memory (size) perspective
The size of the code is increasing for the following reasons:
- The reuse of code is not there: let us take one example, where we have four programs of the same application, and the first ten lines of the program are similar. We can write these ten lines as a discrete function, and it should be accessible by the above four programs as well. And also, if any bug is there, we can modify the line of code in the function rather than the entire code.
- The developers use the logic that might be modified. If one programmer writes code and the file size is up to 250kb, then another programmer could write a similar code using the different logic, and the file size is up to 100kb.
- The developer declares so many functions and variables that might never be used in any portion of the code. Therefore, the size of the program will increase.
Test the performance (Speed, response time) of the program
The application could be slow for the following reasons:
- When logic is used.
- For the conditional cases, we will use or & and adequately.
- Switch case, which means we cannot use nested if, instead of using a switch case.
Black box testing
Black box testing is a technique of software testing which examines the functionality of software without peering into its internal structure or coding. The primary source of black box testing is a specification of requirements that is stated by the customer.
In this method, tester selects a function and gives input value to examine its functionality, and checks whether the function is giving expected output or not. If the function produces correct output, then it is passed in testing, otherwise failed. The test team reports the result to the development team and then tests the next function. After completing testing of all functions if there are severe problems, then it is given back to the development team for correction.
Generic steps of black box testing
- The black box test is based on the specification of requirements, so it is examined in the beginning.
- In the second step, the tester creates a positive test scenario and an adverse test scenario by selecting valid and invalid input values to check that the software is processing them correctly or incorrectly.
- In the third step, the tester develops various test cases such as decision table, all pairs test, equivalent division, error estimation, cause-effect graph, etc.
- The fourth phase includes the execution of all test cases.
- In the fifth step, the tester compares the expected output against the actual output.
- In the sixth and final step, if there is any flaw in the software, then it is cured and tested again.
Techniques Used in Black Box Testing
Decision Table Technique
Decision Table Technique is a systematic approach where various input combinations and their respective system behavior are captured in a tabular form. It is appropriate for the functions that have a logical relationship between two and more than two inputs.
Boundary Value Technique
Boundary Value Technique is used to test boundary values, boundary values are those that contain the upper and lower limit of a variable. It tests, while entering boundary value whether the software is producing correct output or not.
State Transition Technique
State Transition Technique is used to capture the behavior of the software application when different input values are given to the same function. This applies to those types of applications that provide the specific number of attempts to access the application.
All-pair Testing Technique
All-pair testing Technique is used to test all the possible discrete combinations of values. This combinational method is used for testing the application that uses checkbox input, radio button input, list box, text box, etc.
Cause-Effect Technique
Cause-Effect Technique underlines the relationship between a given result and all the factors affecting the result.It is based on a collection of requirements.
Regression Testing
Regression Testing is the process of testing the modified parts of the code and the parts that might get affected due to the modifications to ensure that no new errors have been introduced in the software after the modifications have been made. Regression means return of something and in the software field, it refers to the return of a bug.
Process of Regression testing:
Firstly, whenever we make some changes to the source code for any reasons like adding new functionality, optimization, etc. then our program when executed fails in the previously designed test suite for obvious reasons. After the failure, the source code is debugged in order to identify the bugs in the program. After identification of the bugs in the source code, appropriate modifications are made. Then appropriate test cases are selected from the already existing test suite which covers all the modified and affected parts of the source code. We can add new test cases if required. In the end regression testing is performed using the selected test cases.
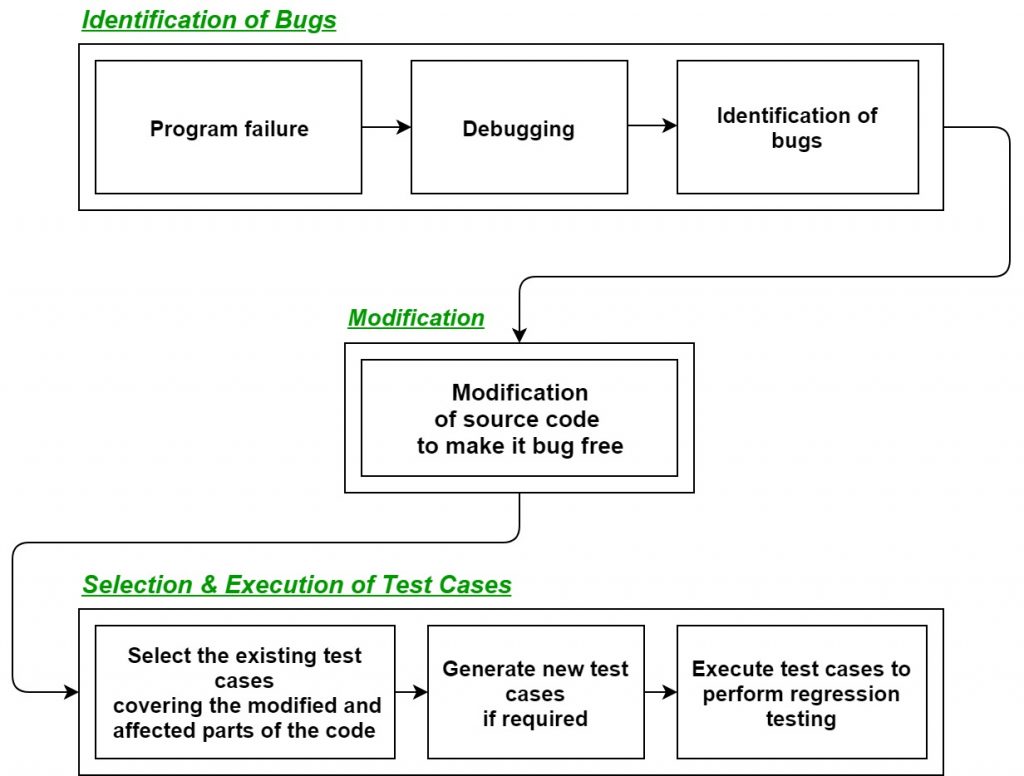
Techniques for the selection of Test cases for Regression Testing:
- Select all test cases: In this technique, all the test cases are selected from the already existing test suite. It is the most simple and safest technique but not much efficient.
- Select test cases randomly: In this technique, test cases are selected randomly from the existing test-suite but it is only useful if all the test cases are equally good in their fault detection capability which is very rare. Hence, it is not used in most of the cases.
- Select modification traversing test cases: In this technique, only those test cases are selected which covers and tests the modified portions of the source code the parts which are affected by these modifications.
- Select higher priority test cases: In this technique, priority codes are assigned to each test case of the test suite based upon their bug detection capability, customer requirements, etc. After assigning the priority codes, test cases with highest priorities are selected for the process of regression testing.
Tools for regression testing: In regression testing, we generally select the test cases from the existing test suite itself and hence, we need not to compute their expected output and it can be easily automated due to this reason. Automating the process of regression testing will be very much effective and time saving.
Most commonly used tools for regression testing are:
- Selenium
- WATIR (Web Application Testing In Ruby)
- QTP (Quick Test Professional)
- RFT (Rational Functional Tester)
- Winrunner
- Silktest
Advantages of Regression Testing:
- It ensures that no new bugs has been introduced after adding new functionalities to the system.
- As most of the test cases used in Regression Testing are selected from the existing test suite and we already know their expected outputs. Hence, it can be easily automated by the automated tools.
- It helps to maintain the quality of the source code.
Disadvantages of Regression Testing:
- It can be time and resource consuming if automated tools are not used.
- It is required even after very small changes in the code.
Unit Testing
Unit testing involves the testing of each unit or an individual component of the software application. It is the first level of functional testing. The aim behind unit testing is to validate unit components with its performance.
A unit is a single testable part of a software system and tested during the development phase of the application software.
The purpose of unit testing is to test the correctness of isolated code. A unit component is an individual function or code of the application. White box testing approach used for unit testing and usually done by the developers.
Whenever the application is ready and given to the Test engineer, he/she will start checking every component of the module or module of the application independently or one by one, and this process is known as Unit testing or components testing.
Objective of Unit Testing:
The objective of Unit Testing is:
- To isolate a section of code.
- To verify the correctness of the code.
- To test every function and procedure.
- To fix bugs early in the development cycle and to save costs.
- To help the developers to understand the code base and enable them to make changes quickly.
- To help with code reuse.
Unit Testing Techniques:
There are 3 types of Unit Testing Techniques. They are
- Black Box Testing: This testing technique is used in covering the unit tests for input, user interface, and output parts.
- White Box Testing: This technique is used in testing the functional behavior of the system by giving the input and checking the functionality output including the internal design structure and code of the modules.
- Gray Box Testing: This technique is used in executing the relevant test cases, test methods, test functions, and analyzing the code performance for the modules.
Unit Testing Tools:
Here are some commonly used Unit Testing tools:
- Jtest
- Junit
- NUnit
- EMMA
- PHPUnit
Advantages of Unit Testing:
- Unit Testing allows developers to learn what functionality is provided by a unit and how to use it to gain a basic understanding of the unit API.
- Unit testing allows the programmer to refine code and make sure the module works properly.
- Unit testing enables testing parts of the project without waiting for others to be completed.
- Early Detection of Issues: Unit testing allows developers to detect and fix issues early in the development process, before they become larger and more difficult to fix.
- Improved Code Quality: Unit testing helps to ensure that each unit of code works as intended and meets the requirements, improving the overall quality of the software.
Disadvantages of Unit Testing:
- The process is time-consuming for writing the unit test cases.
- Unit Testing will not cover all the errors in the module because there is a chance of having errors in the modules while doing integration testing.
- Unit Testing is not efficient for checking the errors in the UI(User Interface) part of the module.
- It requires more time for maintenance when the source code is changed frequently.
- It cannot cover the non-functional testing parameters such as scalability, the performance of the system, etc.
Integration Testing
Integration Testing is defined as a type of testing where software modules are integrated logically and tested as a group. A typical software project consists of multiple software modules, coded by different programmers. The purpose of this level of testing is to expose defects in the interaction between these software modules when they are integrated.
There are four types of integration testing approaches. Those approaches are the following:
1. Big-Bang Integration Testing – It is the simplest integration testing approach, where all the modules are combined and the functionality is verified after the completion of individual module testing.
Advantages:
- It is convenient for small systems.
- Simple and straightforward approach.
- Can be completed quickly.
- Does not require a lot of planning or coordination.
- May be suitable for small systems or projects with a low degree of interdependence between components.
Disadvantages:
- There will be quite a lot of delay because you would have to wait for all the modules to be integrated.
- High-risk critical modules are not isolated and tested on priority since all modules are tested at once.
- Not Good for long projects.
- High risk of integration problems that are difficult to identify and diagnose.
- This can result in long and complex debugging and troubleshooting efforts. 2. Bottom-Up Integration Testing – In bottom-up testing, each module at lower levels are tested with higher modules until all modules are tested. The primary purpose of this integration testing is that each subsystem tests the interfaces among various modules making up the subsystem. This integration testing uses test drivers to drive and pass appropriate data to the lower-level modules.
Advantages:
- In bottom-up testing, no stubs are required.
- A principal advantage of this integration testing is that several disjoint subsystems can be tested simultaneously.
- It is easy to create the test conditions.
- Best for applications that uses bottom up design approach.
- It is Easy to observe the test results.
Disadvantages:
- Driver modules must be produced.
- In this testing, the complexity that occurs when the system is made up of a large number of small subsystems.
- As Far modules have been created, there is no working model can be represented.
3. Top-Down Integration Testing – Top-down integration testing technique is used in order to simulate the behaviour of the lower-level modules that are not yet integrated. In this integration testing, testing takes place from top to bottom. First, high-level modules are tested and then low-level modules and finally integrating the low-level modules to a high level to ensure the system is working as intended.
Advantages:
- Separately debugged module.
- Few or no drivers needed.
- It is more stable and accurate at the aggregate level.
- Easier isolation of interface errors.
- In this, design defects can be found in the early stages.
Disadvantages:
- Needs many Stubs.
- Modules at lower level are tested inadequately.
- It is difficult to observe the test output.
- It is difficult to stub design.
4. Mixed Integration Testing – A mixed integration testing is also called sandwiched integration testing. A mixed integration testing follows a combination of top down and bottom-up testing approaches. In top-down approach, testing can start only after the top-level module have been coded and unit tested. In bottom-up approach, testing can start only after the bottom level modules are ready. This sandwich or mixed approach overcomes this shortcoming of the top-down and bottom-up approaches. It is also called the hybrid integration testing. also, stubs and drivers are used in mixed integration testing.
Advantages:
- Mixed approach is useful for very large projects having several sub projects.
- This Sandwich approach overcomes this shortcoming of the top-down and bottom-up approaches.
- Parallel test can be performed in top and bottom layer tests.
Disadvantages:
- For mixed integration testing, it requires very high cost because one part has a Top-down approach while another part has a bottom-up approach.
- This integration testing cannot be used for smaller systems with huge interdependence between different modules.
Applications:
- Identify the components: Identify the individual components of your application that need to be integrated. This could include the frontend, backend, database, and any third-party services.
- Create a test plan: Develop a test plan that outlines the scenarios and test cases that need to be executed to validate the integration points between the different components. This could include testing data flow, communication protocols, and error handling.
- Set up test environment: Set up a test environment that mirrors the production environment as closely as possible. This will help ensure that the results of your integration tests are accurate and reliable.
- Execute the tests: Execute the tests outlined in your test plan, starting with the most critical and complex scenarios. Be sure to log any defects or issues that you encounter during testing.
- Analyze the results: Analyze the results of your integration tests to identify any defects or issues that need to be addressed. This may involve working with developers to fix bugs or make changes to the application architecture.
System Testing
System Testing includes testing of a fully integrated software system. Generally, a computer system is made with the integration of software (any software is only a single element of a computer system). The software is developed in units and then interfaced with other software and hardware to create a complete computer system. In other words, a computer system consists of a group of software to perform the various tasks, but only software cannot perform the task; for that software must be interfaced with compatible hardware.
To check the end-to-end flow of an application or the software as a user is known as System testing. In this, we navigate (go through) all the necessary modules of an application and check if the end features or the end business works fine, and test the product as a whole system.
System Testing Process: System Testing is performed in the following steps:
- Test Environment Setup: Create testing environment for the better quality testing.
- Create Test Case: Generate test case for the testing process.
- Create Test Data: Generate the data that is to be tested.
- Execute Test Case: After the generation of the test case and the test data, test cases are executed.
- Defect Reporting: Defects in the system are detected.
- Regression Testing: It is carried out to test the side effects of the testing process.
- Log Defects: Defects are fixed in this step.
-
Retest: If the test is not successful then again test is performed. Types of System Testing:
-
Performance Testing: Performance Testing is a type of software testing that is carried out to test the speed, scalability, stability and reliability of the software product or application.
- Load Testing: Load Testing is a type of software Testing which is carried out to determine the behavior of a system or software product under extreme load.
- Stress Testing: Stress Testing is a type of software testing performed to check the robustness of the system under the varying loads.
- Scalability Testing: Scalability Testing is a type of software testing which is carried out to check the performance of a software application or system in terms of its capability to scale up or scale down the number of user request load.
Tools used for System Testing :
- JMeter
- Gallen Framework
- Selenium
Here are some advantages of System Testing:
- Verifies the overall functionality of the system.
- Detects and identifies system-level problems early in the development cycle.
- Helps to validate the requirements and ensure the system meets the user needs.
- Improves system reliability and quality.
-
Facilitates collaboration and communication between development and testing teams. Disadvantages of System Testing :
-
This testing is time consuming process than another testing techniques since it checks the entire product or software.
- The cost for the testing will be high since it covers the testing of entire software.
- It needs good debugging tool otherwise the hidden errors will not be found.
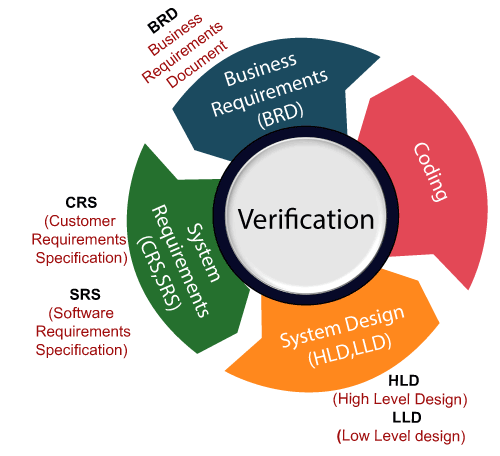
Verification testing
Verification testing includes different activities such as business requirements, system requirements, design review, and code walkthrough while developing a product.
It is also known as static testing, where we are ensuring that "we are developing the right product or not". And it also checks that the developed application fulfilling all the requirements given by the client.
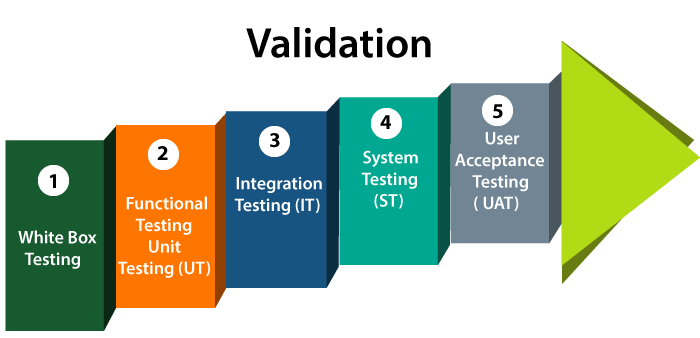
Validation testing
Validation testing is testing where tester performed functional and non-functional testing. Here functional testing includes Unit Testing (UT), Integration Testing (IT) and System Testing (ST), and non-functional testing includes User acceptance testing (UAT).
Validation testing is also known as dynamic testing, where we are ensuring that "we have developed the product right." And it also checks that the software meets the business needs of the client.
Note: Verification and Validation process are done under the V model of the software development life cycle.
| Feature | Verification | Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To check whether we are developing the right product or not. | To check whether the developed product is right. |
| Type of testing | Static testing | Dynamic testing |
| Methods used | Inspections, reviews, walkthroughs | Functional testing, system testing, integration testing, user acceptance testing |
| When performed | During the development cycle | After the development cycle |
| Who performs it | Quality assurance team | Testing team |
| Code execution involved | No | Yes |
| Bugs found | Early in the development phase | Later in the development phase or after deployment |
| Role in quality control | Quality assurance | Quality control |
Software Implementation Techniques
A good system design is to organize the program modules in such a way that are easy to develop and change. Structured design techniques help developers to deal with the size and complexity of programs. Analysts create instructions for the developers about how code should be written and how pieces of code should fit together to form a program.
Software Engineering is the process of designing, building, testing, and maintaining software. The goal of software engineering is to create software that is reliable, efficient, and easy to maintain. System design is a critical component of software engineering and involves making decisions about the architecture, components, modules, interfaces, and data for a software system.
System Design Strategy refers to the approach that is taken to design a software system. There are several strategies that can be used to design software systems, including the following:
- Top-Down Design: This strategy starts with a high-level view of the system and gradually breaks it down into smaller, more manageable components.
- Bottom-Up Design: This strategy starts with individual components and builds the system up, piece by piece.
- Iterative Design: This strategy involves designing and implementing the system in stages, with each stage building on the results of the previous stage.
- Incremental Design: This strategy involves designing and implementing a small part of the system at a time, adding more functionality with each iteration.
- Agile Design: This strategy involves a flexible, iterative approach to design, where requirements and design evolve through collaboration between self-organizing and cross-functional teams.
The choice of system design strategy will depend on the particular requirements of the software system, the size and complexity of the system, and the development methodology being used. A well-designed system can simplify the development process, improve the quality of the software, and make the software easier to maintain.
Importance :
- If any pre-existing code needs to be understood, organized, and pieced together.
- It is common for the project team to have to write some code and produce original programs that support the application logic of the system.
There are many strategies or techniques for performing system design. They are:
- Bottom-up approach:
The design starts with the lowest level components and subsystems. By using these components, the next immediate higher-level components and subsystems are created or composed. The process is continued till all the components and subsystems are composed into a single component, which is considered as the complete system. The amount of abstraction grows high as the design moves to more high levels.
By using the basic information existing system, when a new system needs to be created, the bottom-up strategy suits the purpose.

Advantages:
- The economics can result when general solutions can be reused.
- It can be used to hide the low-level details of implementation and be merged with the top-down technique.
Disadvantages:
- It is not so closely related to the structure of the problem.
- High-quality bottom-up solutions are very hard to construct.
- It leads to the proliferation of ‘potentially useful’ functions rather than the most appropriate ones.
Top-down approach: Each system is divided into several subsystems and components. Each of the subsystems is further divided into a set of subsystems and components. This process of division facilitates forming a system hierarchy structure. The complete software system is considered a single entity and in relation to the characteristics, the system is split into sub-systems and components. The same is done with each of the sub-systems.
This process is continued until the lowest level of the system is reached. The design is started initially by defining the system as a whole and then keeps on adding definitions of the subsystems and components. When all the definitions are combined together, it turns out to be a complete system.
For the solutions of the software that need to be developed from the ground level, a top-down design best suits the purpose.
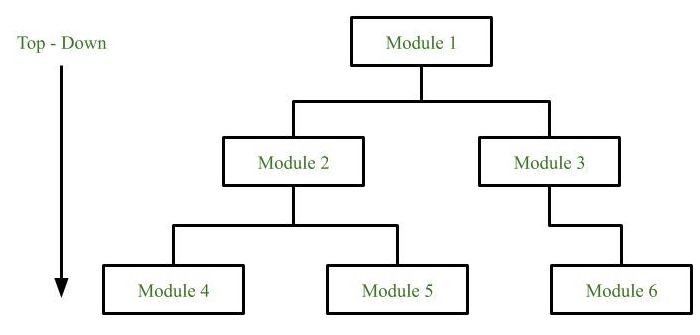
Advantages:
- The main advantage of the top-down approach is that its strong focus on requirements helps to make a design responsive according to its requirements.
Disadvantages:
- Project and system boundaries tend to be application specification-oriented. Thus it is more likely that the advantages of component reuse will be missed.
- The system is likely to miss, the benefits of a well-structured, simple architecture.
- Hybrid Design:
It is a combination of both top-down and bottom-up design strategies. In this, we can reuse the modules.
Advantages of using a System Design Strategy:
- Improved quality: A well-designed system can improve the overall quality of the software, as it provides a clear and organized structure for the software.
- Ease of maintenance: A well-designed system can make it easier to maintain and update the software, as the design provides a clear and organized structure for the software.
- Improved efficiency: A well-designed system can make the software more efficient, as it provides a clear and organized structure for the software that reduces the complexity of the code.
- Better communication: A well-designed system can improve communication between stakeholders, as it provides a clear and organized structure for the software that makes it easier for stakeholders to understand and agree on the design of the software.
- Faster development: A well-designed system can speed up the development process, as it provides a clear and organized structure for the software that makes it easier for developers to understand the requirements and implement the software.
Disadvantages of using a System Design Strategy:
- Time-consuming: Designing a system can be time-consuming, especially for large and complex systems, as it requires a significant amount of documentation and analysis.
- Inflexibility: Once a system has been designed, it can be difficult to make changes to the design, as the process is often highly structured and documentation-intensive.
References
- https://www.javatpoint.com/white-box-testing
- https://www.javatpoint.com/black-box-testing
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/software-engineering-regression-testing/
- https://www.browserstack.com/guide/regression-testing
- https://www.javatpoint.com/unit-testing
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/unit-testing-software-testing/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/software-engineering-integration-testing/?ref=lbp
- https://www.guru99.com/integration-testing.html
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/system-testing/?ref=lbp
- https://www.javatpoint.com/system-testing
- https://www.javatpoint.com/verification-and-validation-testing
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/software-engineering-system-design-strategy/
- https://www.brainkart.com/article/Internal-and-external-views-of-Testing_9085/
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/external-vs-internal-testing-mariya-novikava
- https://www.scaler.com/topics/fundamentals-of-software-testing/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/software-testing-basics/